Binder学习-实践
实例
创建一个AIDL HelloService
interface HelloService {
String sayHello();
}
创建一个Service MyService
public class MyService extends Service {
//通过Stub与Binder通信
private final HelloService.Stub mBinder = new HelloService.Stub() {
@Override
public String sayHello() throws RemoteException {
return "hello";
}
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
}
创建一个Activity ClientActivity
public class ClientActivity extends Activity {
HelloService helloService;
ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//通过proxy和binder通信
helloService = HelloService.Stub.asInterface(service);
try{
String s = helloService.sayHello();
Log.d("Client", s);
}catch (RemoteException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
helloService = null;
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_client);
Log.d("ClientActivity", "Attempting to bind service...");
Intent intent = new Intent(getBaseContext(), MyService.class);
bindService(intent,connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unbindService(connection);
}
}
不同进程间的服务调用流程
- 观察
ClientActivity中onServiceConnected对象,查看其service参数类型如下:
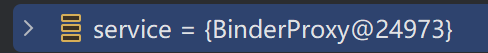 可以看到,接收到的是一个BinderProxy类型的对象。通过
可以看到,接收到的是一个BinderProxy类型的对象。通过
helloService = HelloService.Stub.asInterface(service);
将返回一个Proxy对象 helloService,根据HelloService.Stub.asInterface的源码可以看到
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof com.example.mybindertest.HelloService))) {
return ((com.example.mybindertest.HelloService)iin);
}
return new com.example.mybindertest.HelloService.Stub.Proxy(obj);
如果没有找到一个本地的HelloService接口的实例,则返回一个HelloService.Stub.Proxy的对象,如下:

执行helloService.sayHello方法:
public java.lang.String sayHello() throws android.os.RemoteException
{
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
java.lang.String _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_sayHello, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readString();
}
finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
可以看到其调用了BinderProxy的transact方法将请求的Parcel类型对象_data, _reply发送给binder。查看BinderProxy的transact方法,可以看到如下代码:
final boolean result = transactNative(code, data, reply, flags);
其调用了transactNative方法:
/**
* Native implementation of transact() for proxies */
public native boolean transactNative(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException;
可以看到该方法为一个native方法。
- 给MyService的sayHello方法打上断点,观察其调用栈,可以看到:
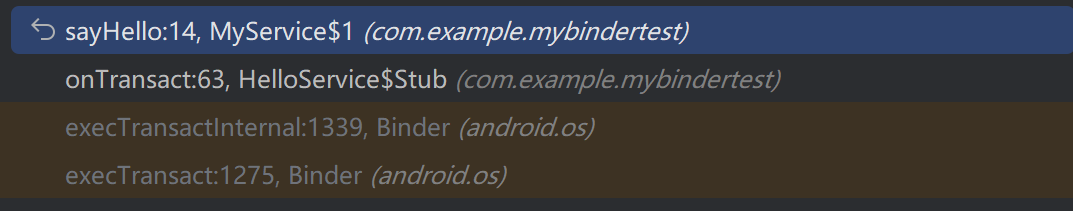 查看
查看Binder.execTransact方法
// Entry point from android_util_Binder.cpp's onTransact.
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private boolean execTransact(int code, long dataObj, long replyObj,
int flags) {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(dataObj);
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain(replyObj);
final long origWorkSource = callingUid == -1
? -1 : ThreadLocalWorkSource.setUid(callingUid);
try {
return execTransactInternal(code, data, reply, flags, callingUid);
} finally {
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
if (callingUid != -1) {
ThreadLocalWorkSource.restore(origWorkSource);
}
}
}
可以看到其对应C++ native android_util_Binder的onTransact方法,并调用了自己的execTransactInternal方法
private boolean execTransactInternal(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags,
int callingUid) {
...
if ((flags & FLAG_COLLECT_NOTED_APP_OPS) != 0 && callingUid != -1) {
AppOpsManager.startNotedAppOpsCollection(callingUid);
try {
res = onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
} finally {
AppOpsManager.finishNotedAppOpsCollection();
}
} else {
res = onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
可以看到,其调用了onTransact方法,而onTransact方法由HelloServie$Stub实现:
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException
{
//...
switch (code)
{
case TRANSACTION_sayHello:
{
java.lang.String _result = this.sayHello();
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeString(_result);
break;
}
default:
{
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
}
return true;
}
对于创建的HelloService的AIDL,自动创建了一个HelloService的接口,并为其创建了Stub和Stub.Proxy两个内部类。可以看到收到TRANSACTION_sayHello的code后,调用其sayHello方法,并将结果写入reply中
private final HelloService.Stub mBinder = new HelloService.Stub() {
@Override
public String sayHello() throws RemoteException {
return "hello";
}
};
在MyService中重写了Stub的sayHello方法
当Service和Activity运行在一个进程中的调用流程
- 删除
AndroidManifest.xml中将MyService和ClientActivity设置到两个进程的设置 - 调试
onServiceConnected方法,可以看到,传入的service类型变为HelloService$Stub类型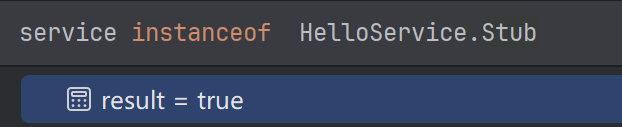
根据HelloService.Stub.asInterface()方法,此时queryLocalInterface返回该Stub类型对象
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof com.example.mybindertest.HelloService))) {
return ((com.example.mybindertest.HelloService)iin);
}
于是,当调用helloService.sayHello方法时,实际上是直接调用了在MyService中创建的Stub类型对象mbinder中重写的sayHello方法